
Cardiopulmonary interaction and pathobiology of pulmonary hypertension... Download Scientific
The S 1 Q 3 T 3 sign (prominent S wave in lead I, Q wave and inverted T wave in lead III) is a sign of acute cor pulmonale (acute pressure and volume overload of the right ventricle because of pulmonary hypertension) and reflects right ventricular strain.1 This electrocardiogram (ECG) finding is present in 15% to 25% of patients ultimately diagnosed with pulmonary emboli (PE).2 Any cause of.
Pulmonary Embolism • LITFL • CCC Respiratory
Reviewed and revised 7 January 2016. OVERVIEW. Thrombolysis is an established therapy for massive pulmonary embolism; The use of thrombolytics for the treatment of submassive PE is controversial — the limited documented benefit (e.g. improved hemodynamics, potential for less chronic pulmonary hypertension) must be weighed against the increased risk of life-threatening hemorrhage and the.

Pulmonary Embolus pondering • LITFL • Clinical Case discussion
Pulmonary embolism (PTE, PE) ranges from asymptomatic to a life threatening catastrophe. PE occurs when a deep vein thrombosis migrates to the pulmonary arterial tree.. Cadogan M. CXR eponyms in pulmonary embolism. LITFL; Journal articles. Agnelli G, Becattini C. Acute pulmonary embolism. N Engl J Med. 2010 Jul 15;363(3):266-74.
Pulmonary Embolism Treatment in Denver, CO MIPS Cardiology Center
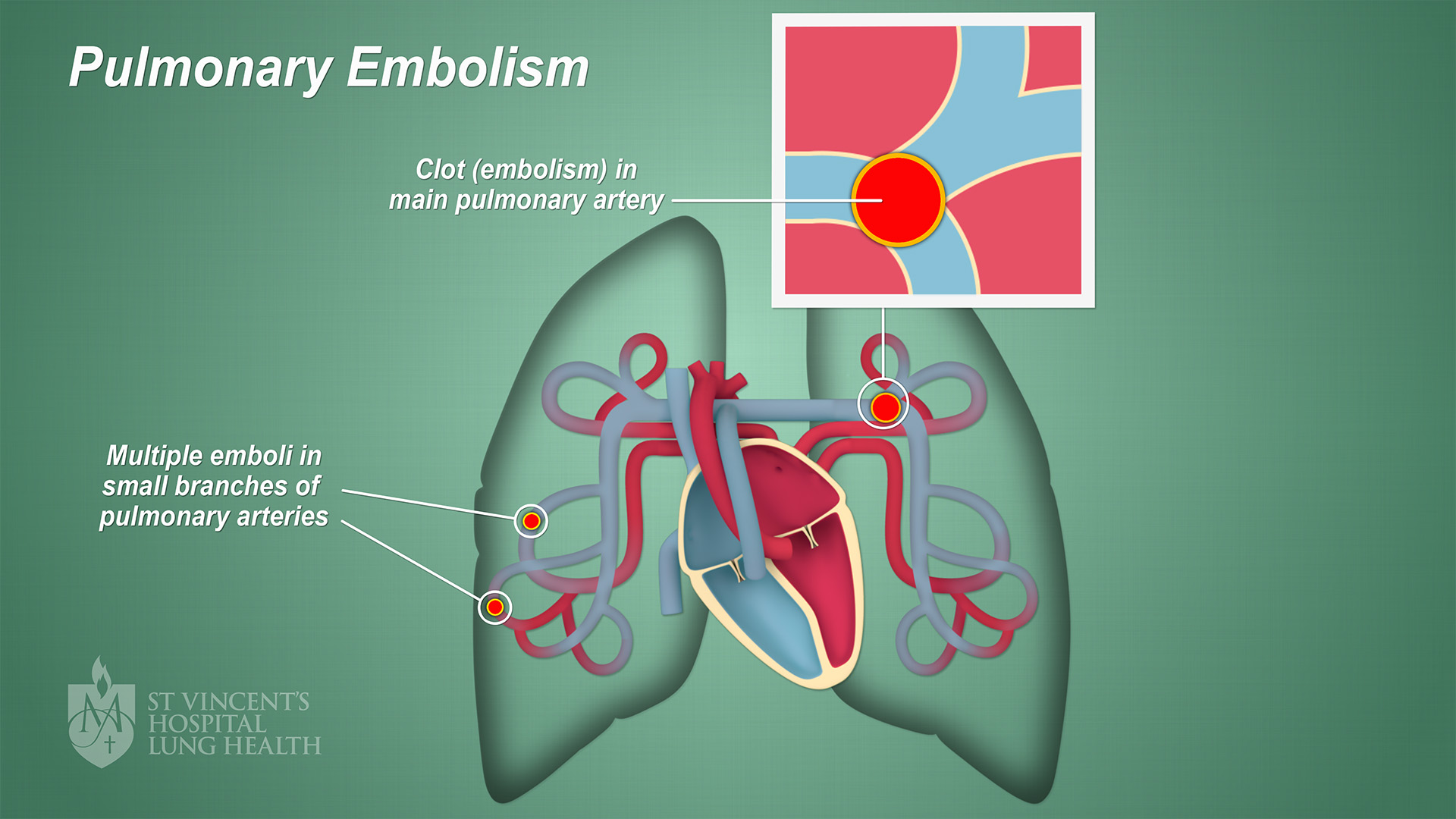
Pulmonary embolism occurs when embolic venous thrombi are caught within the branching lung vasculature. These thrombi often develop within the leg or pelvic veins, and approximately half of all.

Ecg Changes In Pulmonary Embolism Litfl Ecg Library Images
A pulmonary embolism occurs when a clump of material, most often a blood clot, gets stuck in an artery in the lungs, blocking the flow of blood. Blood clots most commonly come from the deep veins of your legs, a condition known as deep vein thrombosis. In many cases, multiple clots are involved. The portions of lung served by each blocked.
Pulmonary Embolism Pulmonary Embolism Aps Foundation Of America Inc / Unlike the wells score
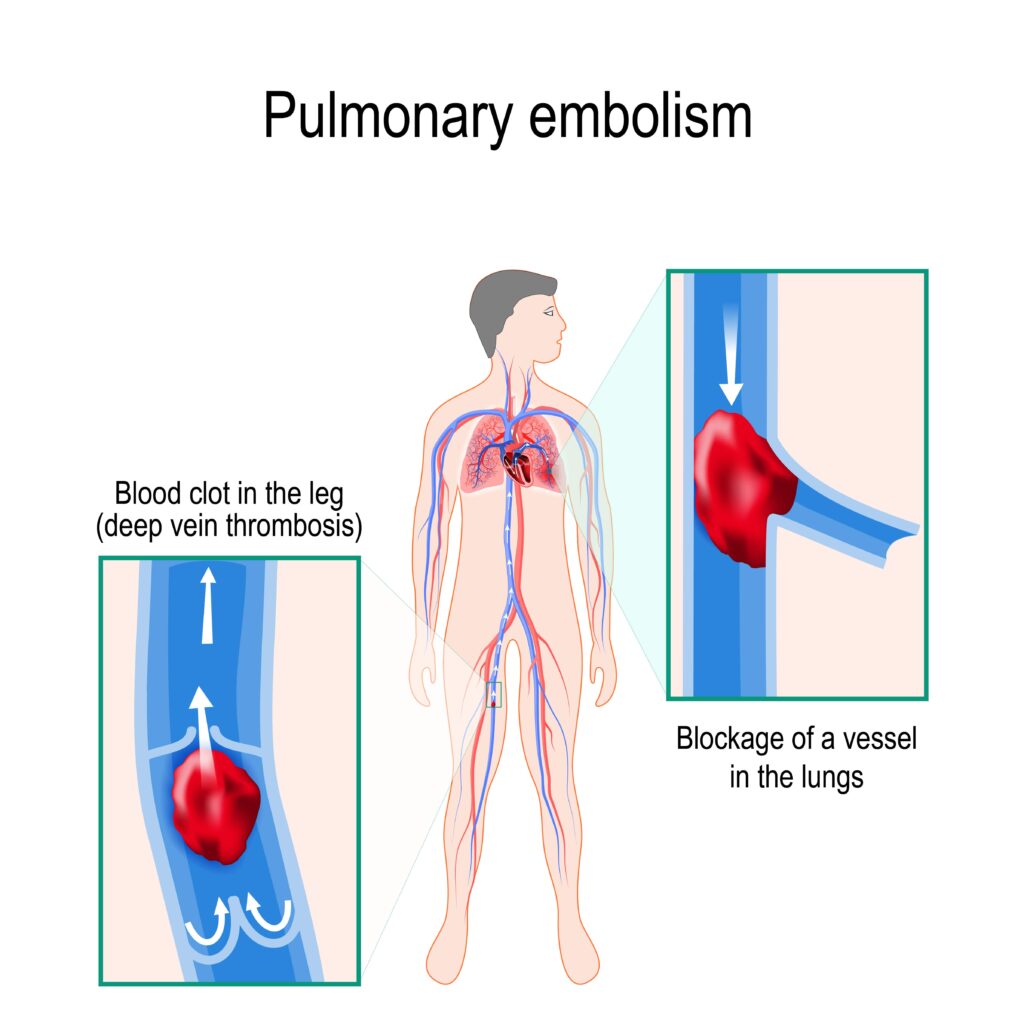
A pulmonary embolism (PE) is a blood clot that develops in a blood vessel elsewhere in the body (often the leg), travels to an artery in the lung, and suddenly forms a blockage of the artery. Abnormal blood clots can form due to problems such as "sluggish" blood flow through the veins, an abnormality in clot forming factors, and/or an injury to.

CXR eponyms in pulmonary embolism • LITFL • Medical Eponym Library
Pulmonary Embolism: Next Generation - Lauren Westafer. Lauren Westafer introduces the concept of a new generation of pulmonary embolism (PE). What was once considered a deadly disease process now carries a mortality rate of <3%, which may be driven by overtesting as well as overdiagnosis.
Pulmonary Embolism • LITFL • CCC Respiratory
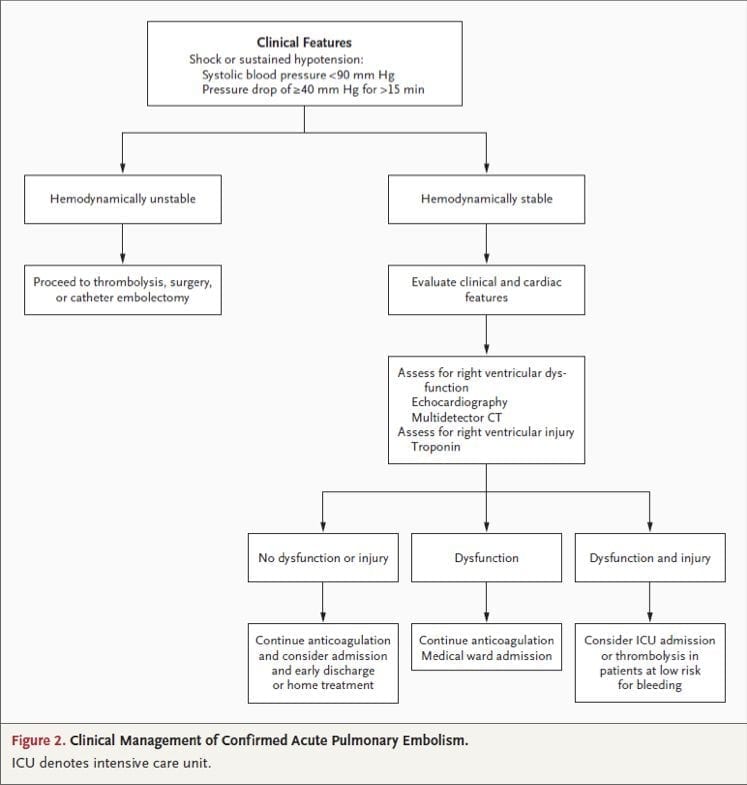
Acute pulmonary embolism occurs frequently and may cause death or serious disability. 1 Case fatality rates vary widely, 2,3 but approximately 10% of all patients with acute pulmonary embolism die.

Pulmonary Embolism Causes, Signs & Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment
The ECG changes associated with acute pulmonary embolism may be seen in any condition that causes acute pulmonary hypertension, including hypoxia causing pulmonary hypoxic vasoconstriction.. Editor-in-chief of the LITFL ECG Library. Twitter: @rob_buttner. 3 Comments . Erin . March 13, 2019 / 01:30 Reply. Hi Dr. Burns, can you list the.

What Is Pulmonary Embolism Causes, Symptoms and Diagnosing
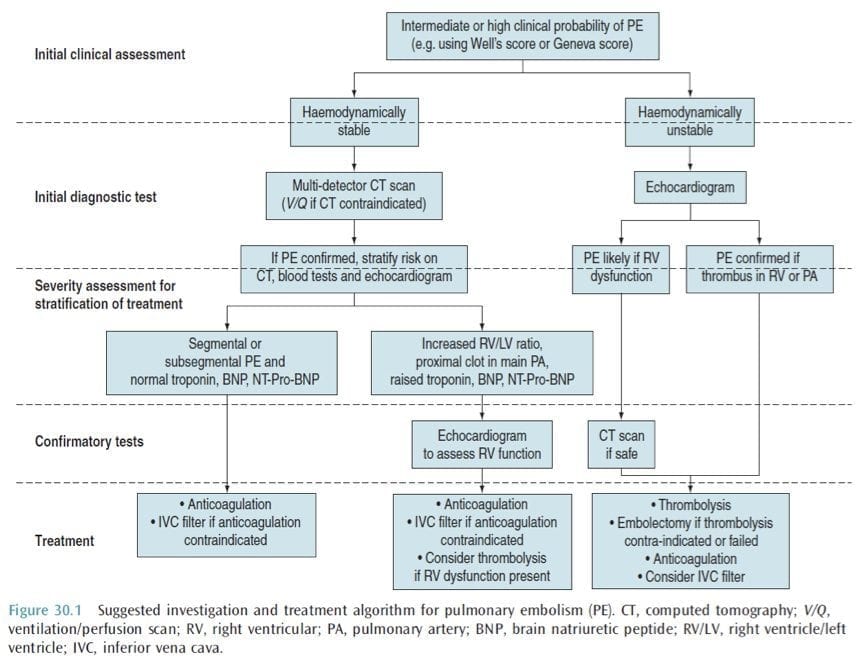
This document follows the previous ESC guidelines focusing on the clinical management of pulmonary embolism (PE) published in 2000, 2008, and 2014. Many recommendations have been retained or their validity has been reinforced; however, new data have extended or modified our knowledge in respect of the optimal diagnosis, assessment, and.
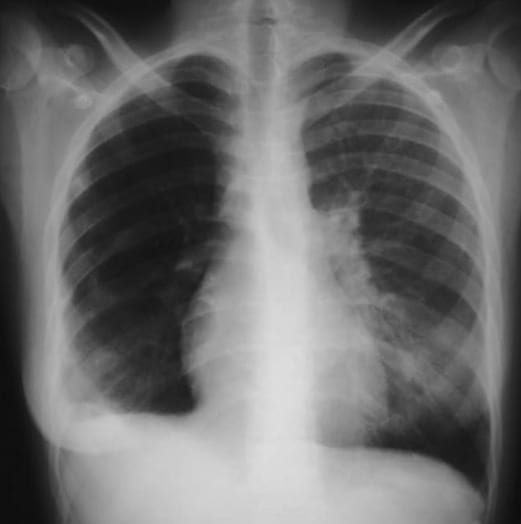
Westermark sign • LITFL • Medical Eponym Library
right ventricular dilation & strain general comments. RV dilation is a prerequisite for either submassive or massive PE.; Whenever possible, comparison should be made to prior echocardiography, CT scans, and/or EKGs.(Chronic right ventricular dysfunction suggests chronic pulmonary hypertension, rather than submassive PE).CT scan is usually immediately available.

The ECG’s of Pulmonary Embolism Resus
Acute pulmonary embolism (PE) is the third leading cause of death globally, yet the majority of patients have a low mortality rate and can be treated by anticoagulation alone.1 Reperfusion therapy (thrombolysis or embolectomy) is indicated for high-risk PE, defined as hemodynamic instability from PE, and for certain intermediate-risk patients, particularly those who deteriorate while receiving.
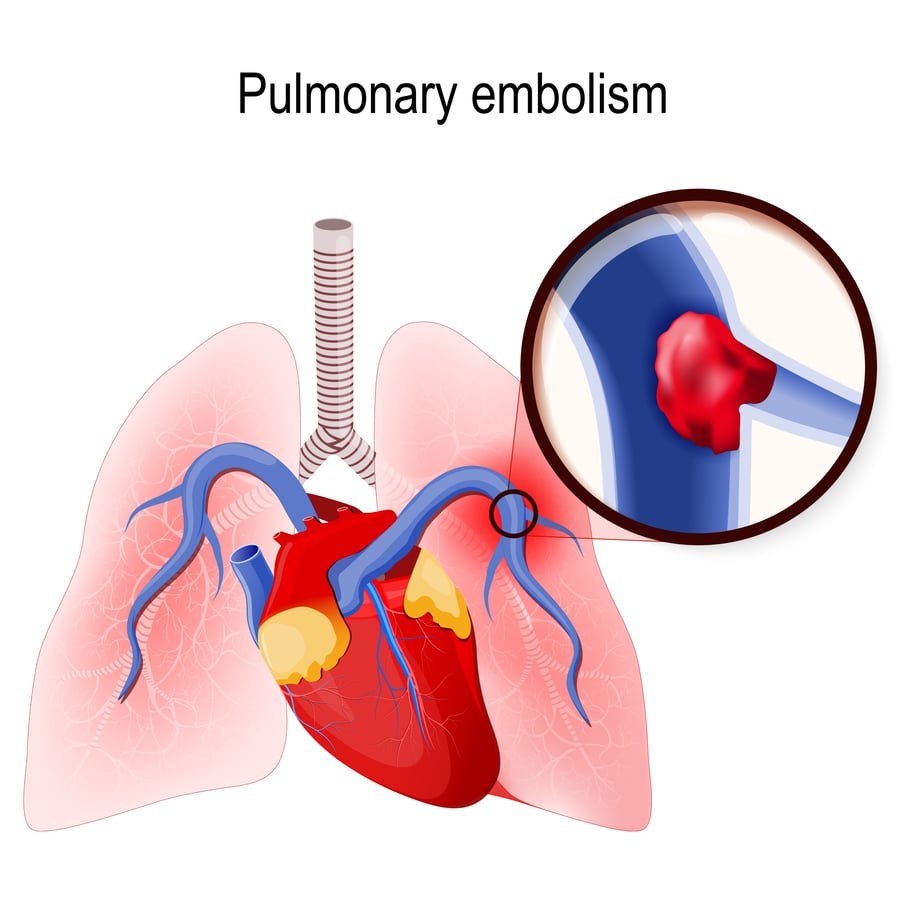
Pulmonary Embolism What You Need to Know
Fengler BT, Brady WJ (2009) Fibrinolytic Therapy in Pulmonary Embolism: an Evidence Based Algorithm. American Journal of Emergency Medicine. 27 84-89 [PMID 19041539] Roy P et al (2005) Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Strategies for the Diagnosis of Suspected Pulmonary Embolism. BMJ 331:259 [PMID 16052017]

Pulmonary Embolism What is it and Why Does it Occur? Video & Lesson Transcript
Pulmonary embolism (PE) occurs when there is a disruption to the flow of blood in the pulmonary artery or its branches by a thrombus that originated somewhere else. In deep vein thrombosis (DVT), a thrombus develops within the deep veins, most commonly in the lower extremities. PE usually occurs when a part of this thrombus breaks off and enters the pulmonary circulation. Very rarely, PE can.
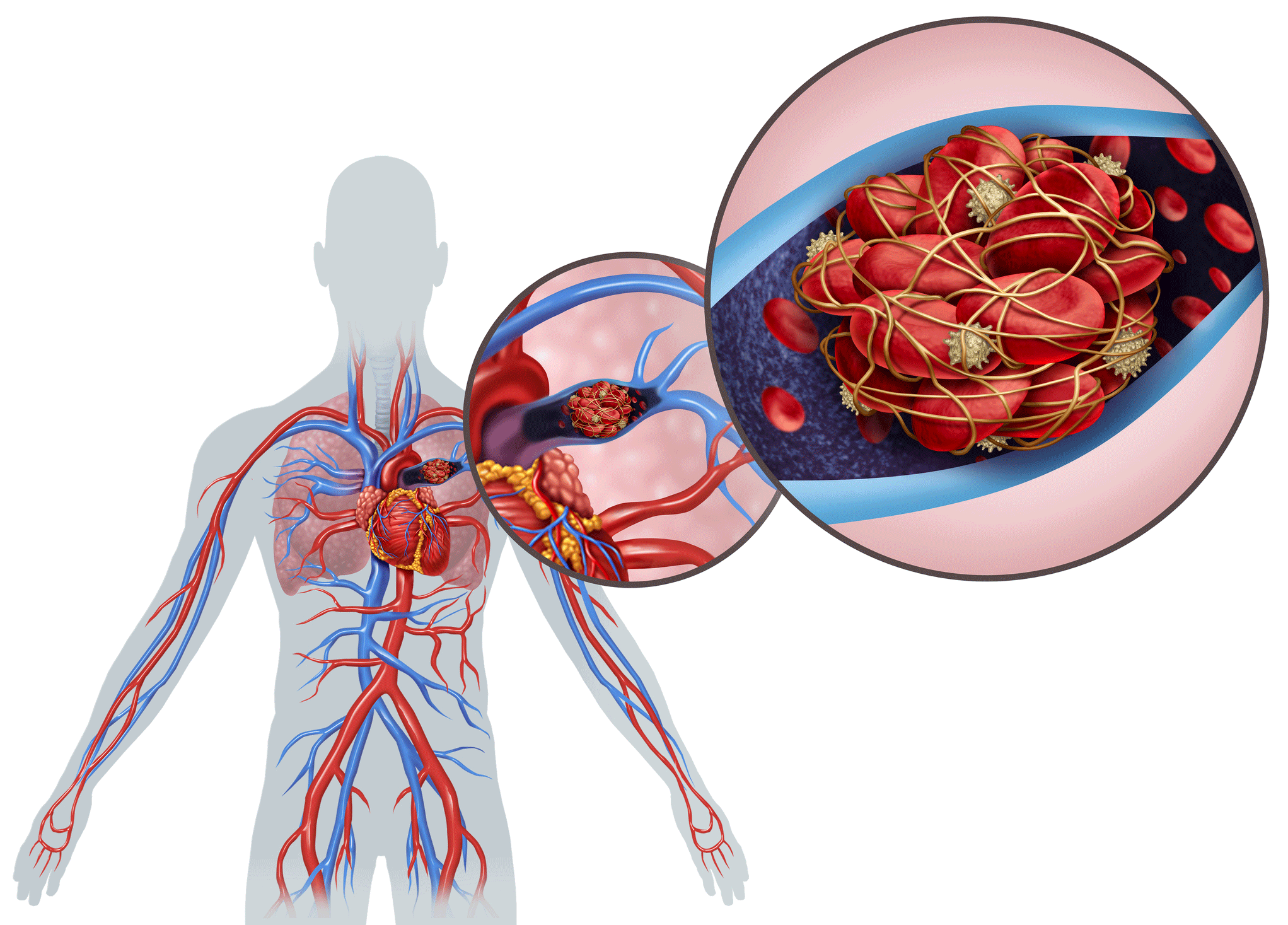
What Is a Pulmonary Embolism? YourCareEverywhere
The value of the ECG for the diagnosis of pulmonary embolism (PE) is debatable. Once the diagnosis of PE has been established, however, the ECG could allow the massive forms to be distinguished. The purpose of our study was to analyze the ECG signs in patients hospitalized for PE in a cardiology unit.

Pulmonary Embolism (PE) Causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment
Wells PS, Anderson DR, Rodger M, et al. Derivation of a simple clinical model to categorize patients probability of pulmonary embolism: increasing the models utility with the SimpliRED D-dimer. Thromb Haemost 2000;83:416-20. Le Gal G, Righini M, Roy PM, et al. Prediction of pulmonary embolism in the emergency department: the revised Geneva score.